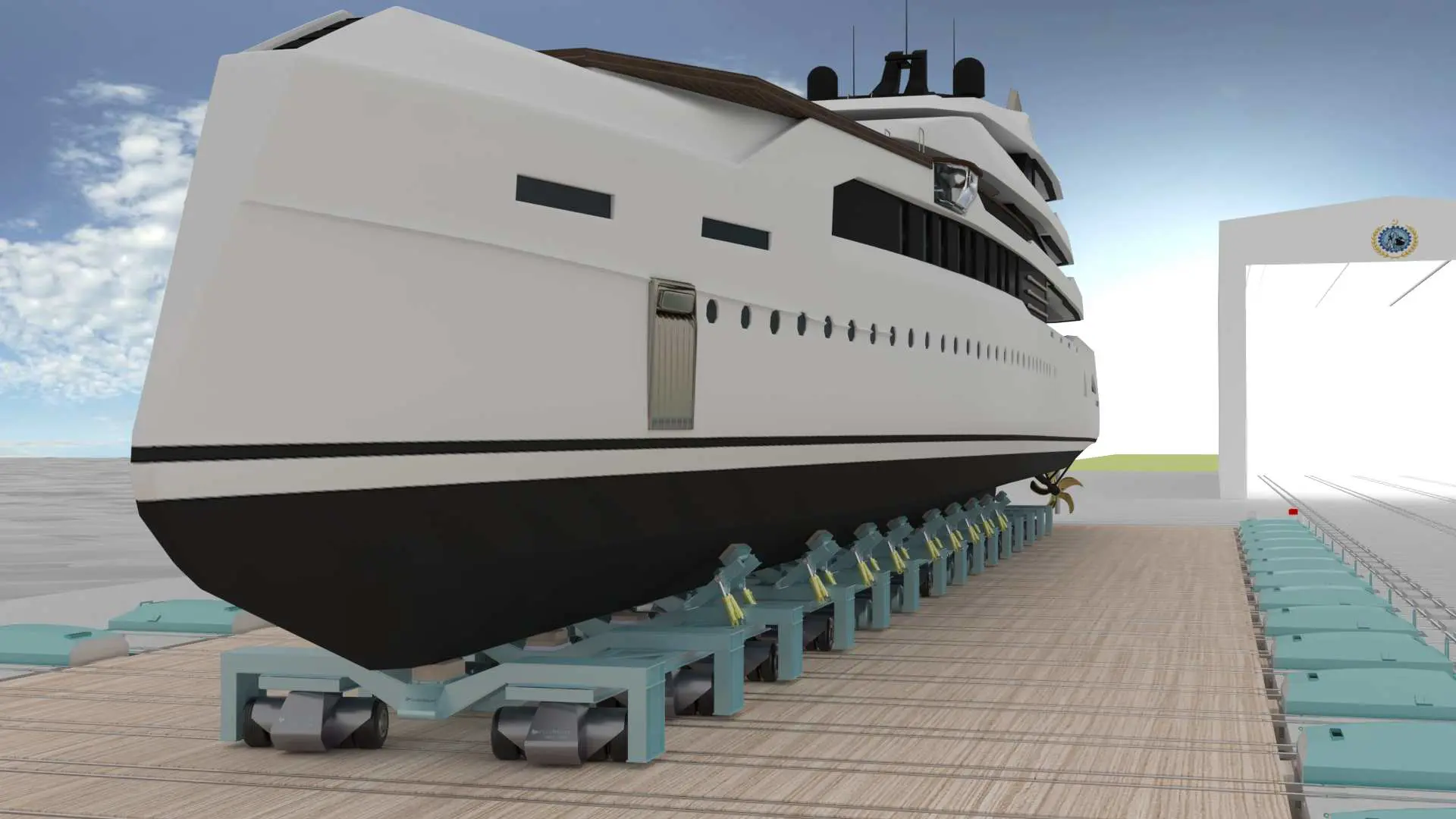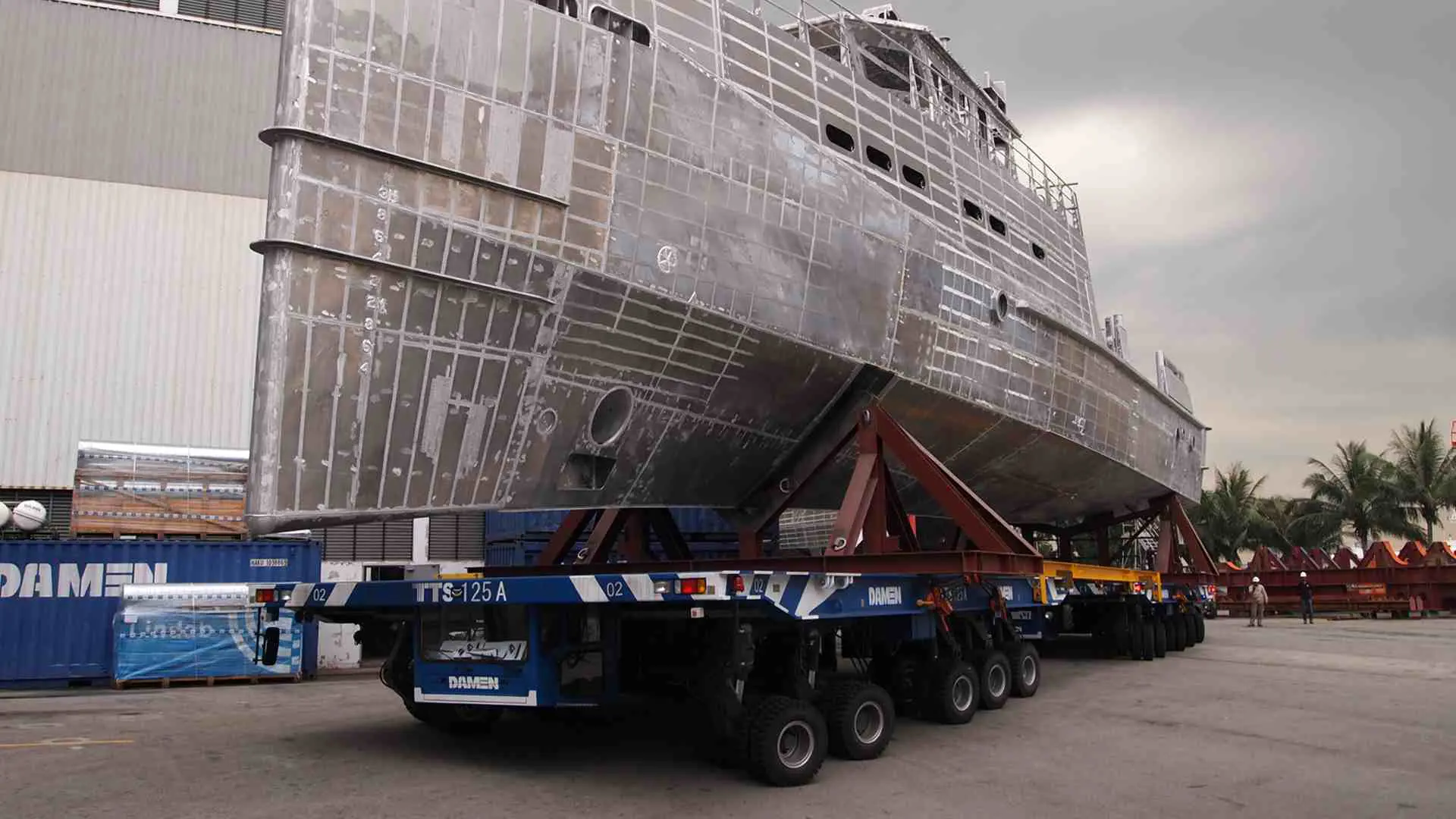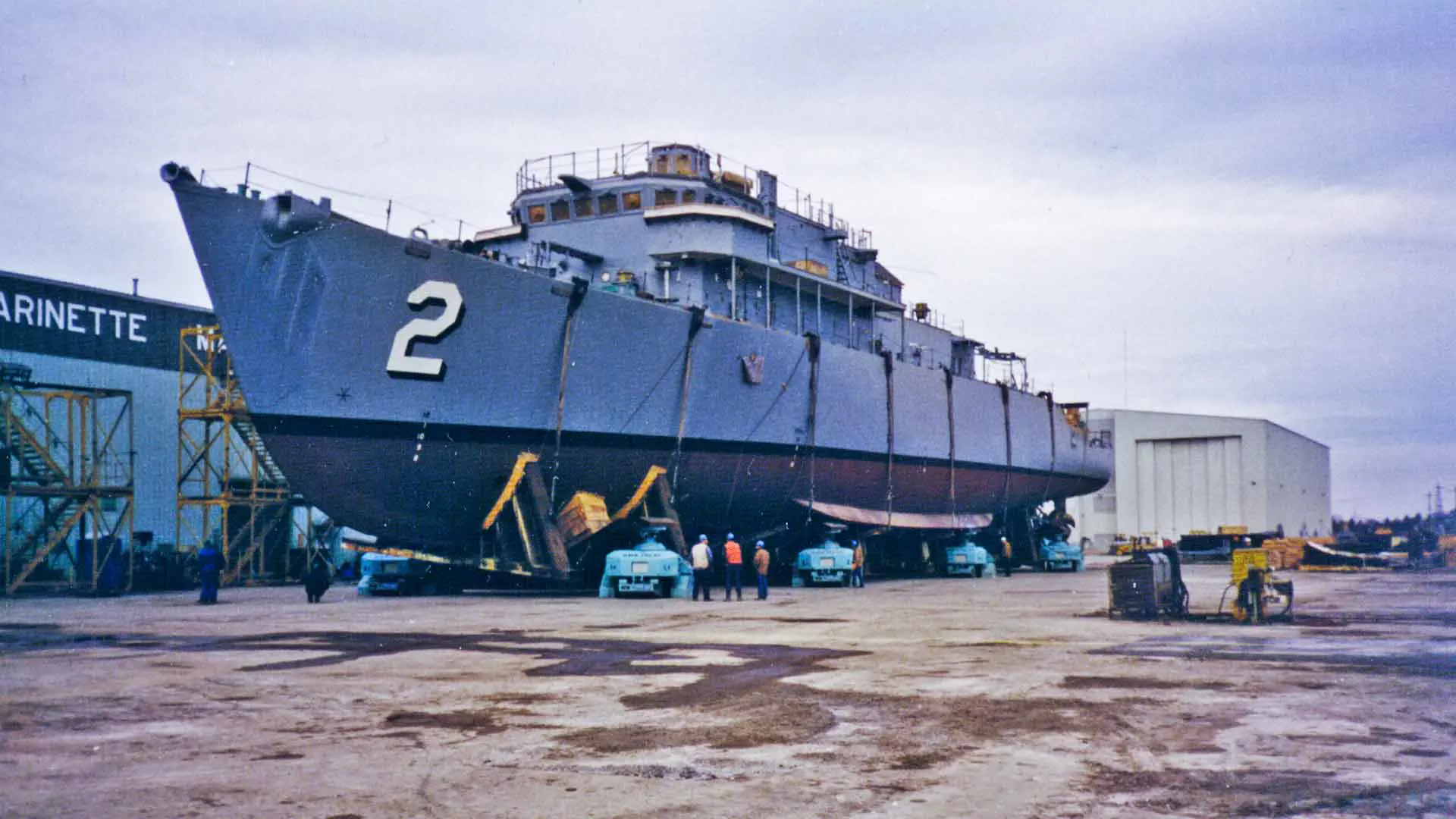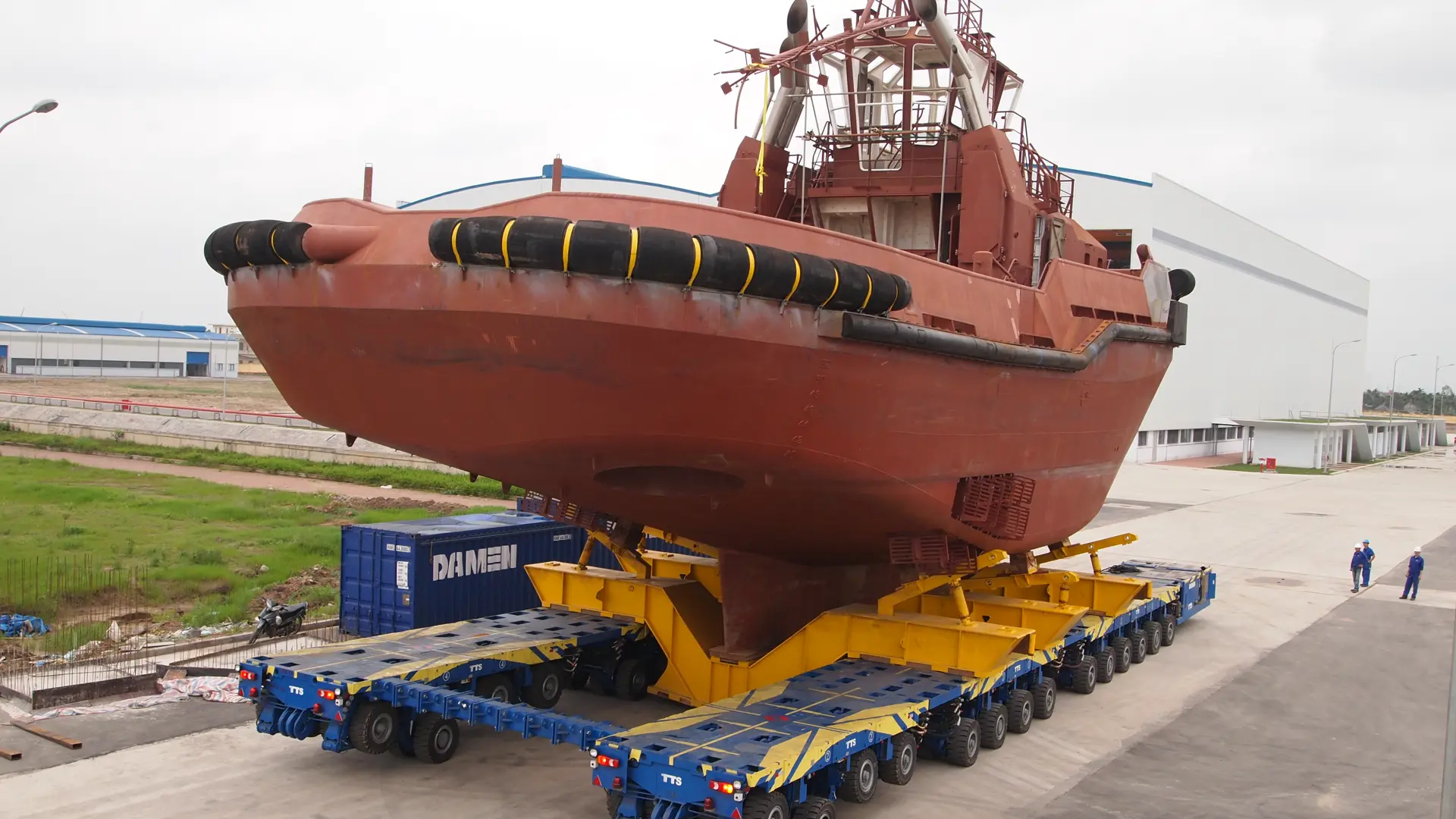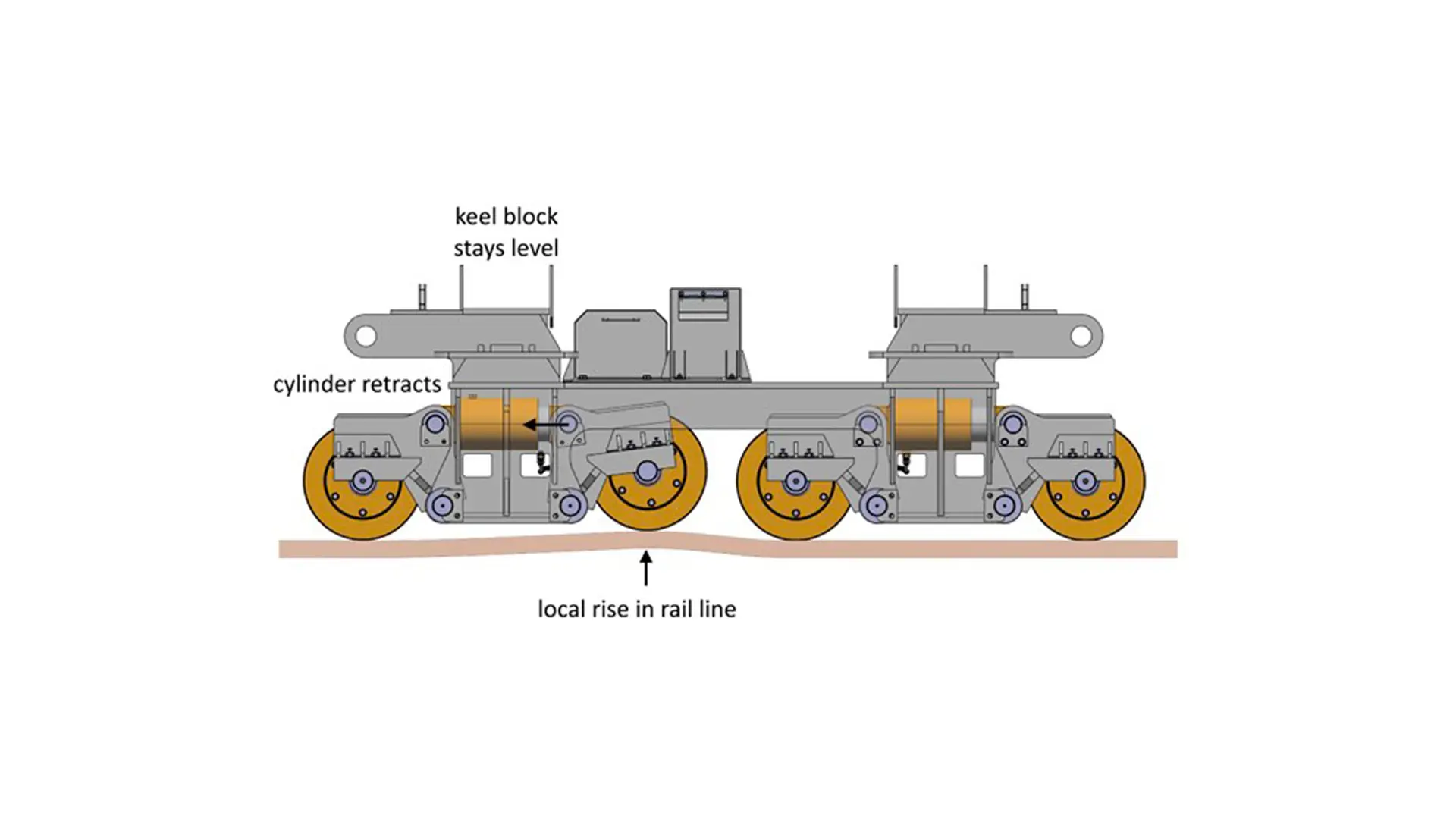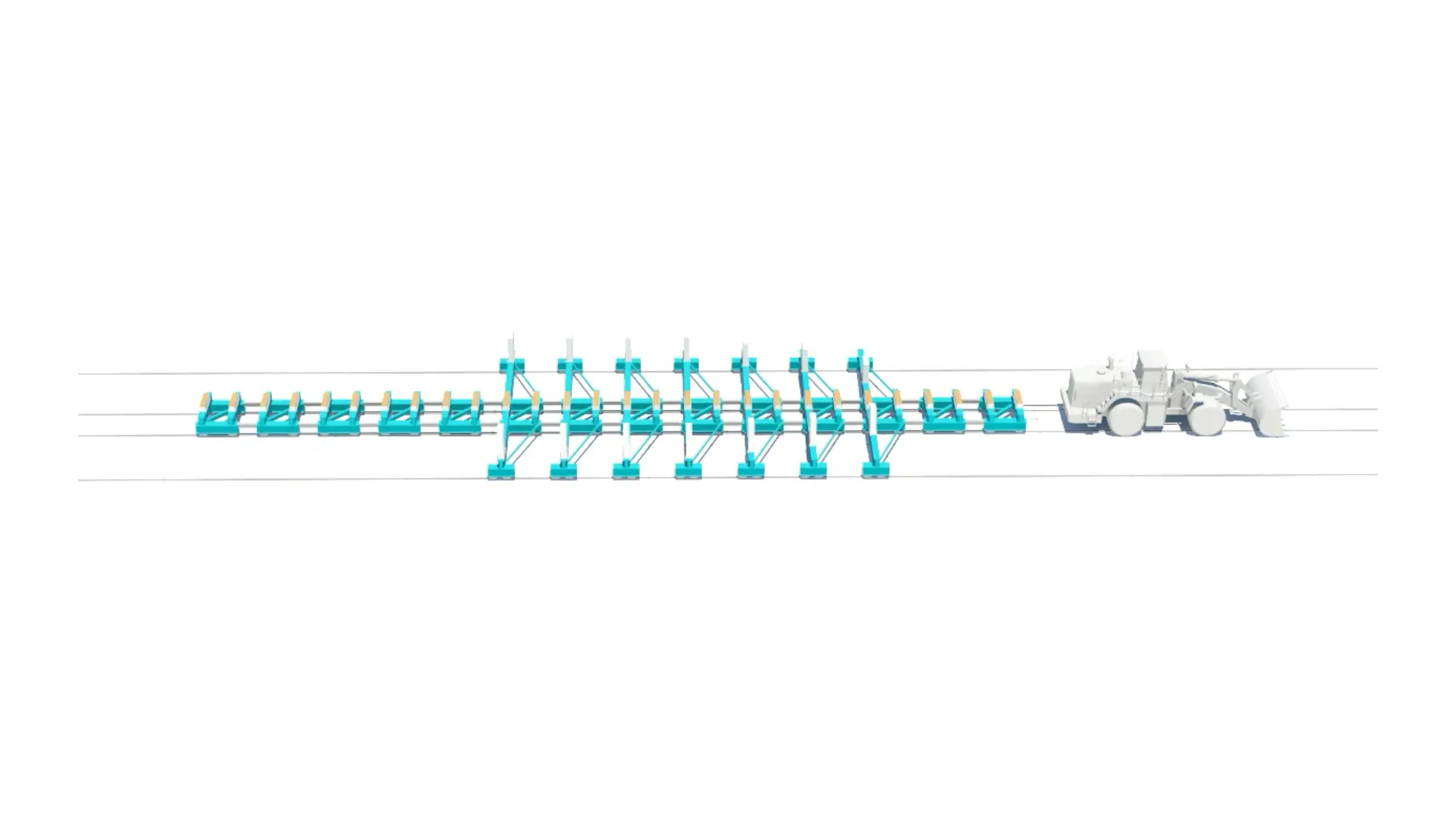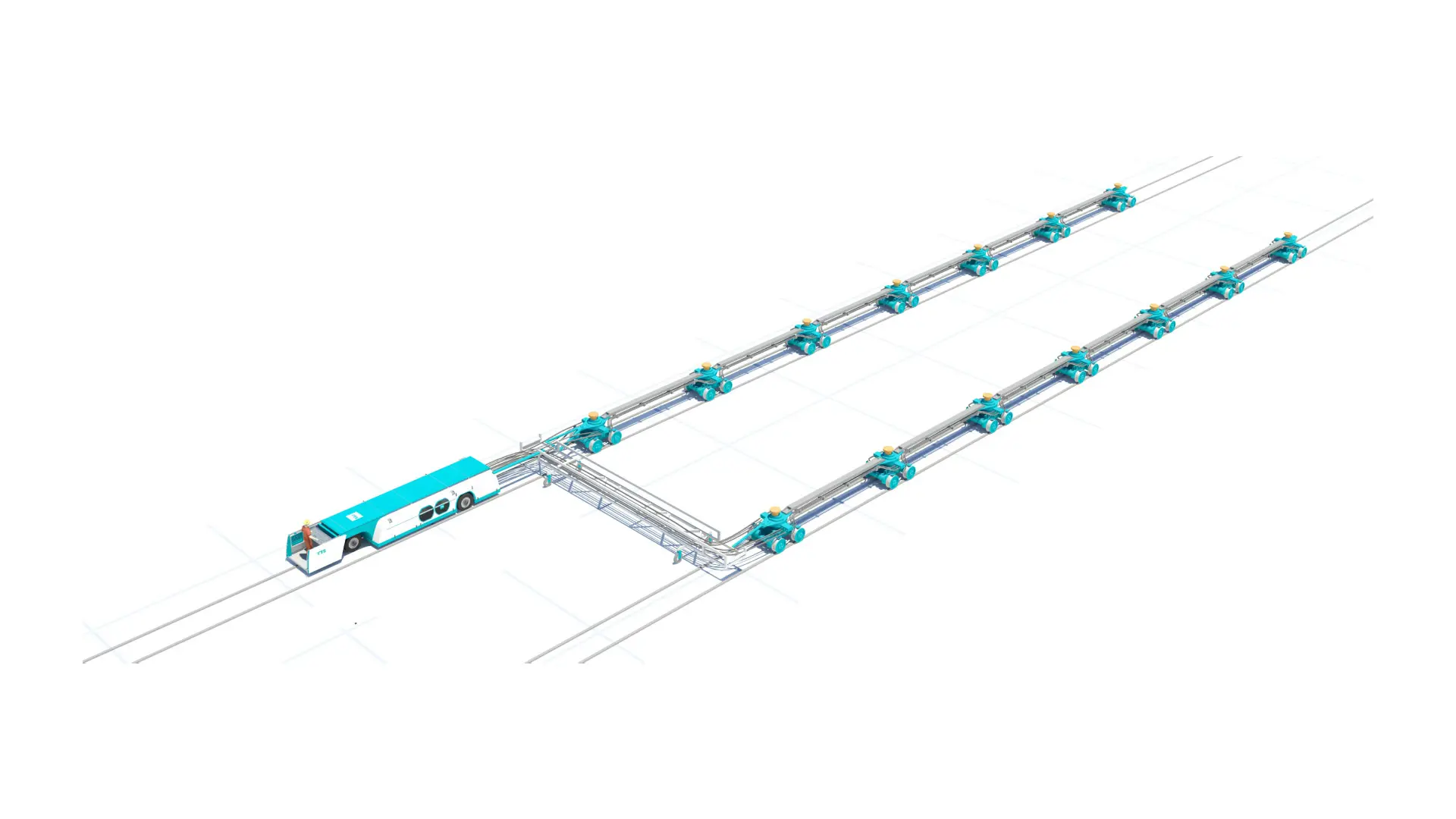
Fluid-bed Transfer System
- Work load area up to 40 000 tons
- Rails
- Fluid bed
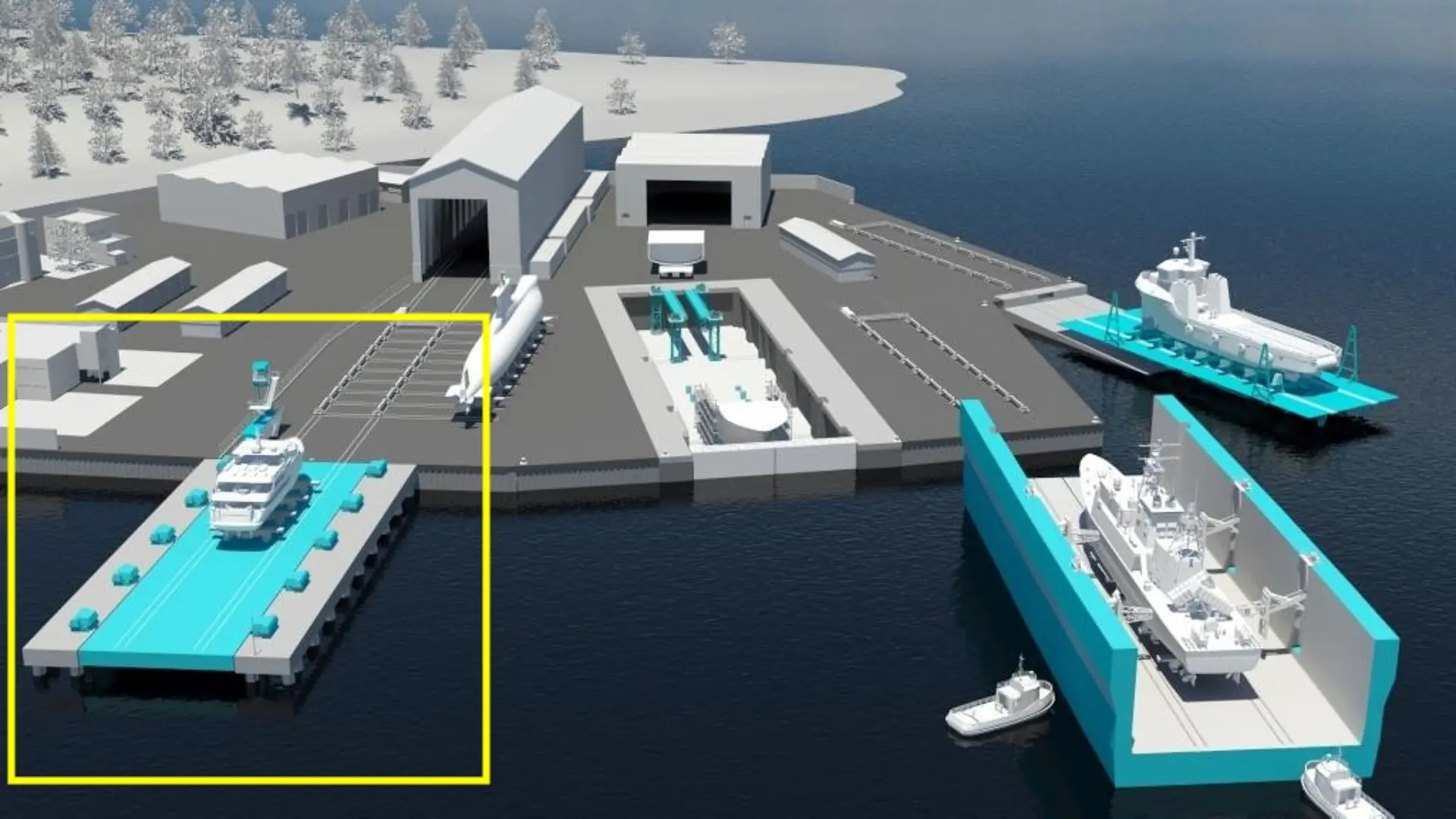
There are two primary types of platforms within shiplift systems: the modern, often referred to as the SAFE type of Rigid platform developed in the 1980s, and the older Articulated platform, which dates back to the 1950s. The key distinction in their construction lies in the fact that Articulated platforms incorporate hinged designs, allowing for flexibility, whereas Rigid platforms, sometimes called hybrid platforms, are characterized by their fully welded structures.
This structural difference results in two notable functional disparities:
Due to these safety differences, most suppliers today favor the Rigid platform. It's important to note that under optimal conditions, the safety performance of both platforms is comparable. Nevertheless, contemporary safety standards prioritize the need for built-in redundancy, a requirement that the hinged construction of Articulated platforms fails to meet.
The Articulated platform, with its straightforward hinged design, offers the benefit of requiring simpler machinery for operation. In contrast, a Rigid platform demands more complex calculations and control mechanisms. However, thanks to advancements in Finite Element Method (FEM) analysis and servo motor technology, Rigid platforms boast several unique advantages: